In the intricate world of medical billing, precision and efficiency are fundamental to ensuring that healthcare practices remain financially healthy. Among the various steps that contribute to a well-functioning billing system, charge entry stands out as one of the most critical components. It is often overlooked, but mistakes at this stage can lead to rejected claims, delayed reimbursements, and revenue losses that can significantly impact a practice’s bottom line. This blog delves into the charge entry process, its importance, and why it is crucial for the smooth operation of revenue cycle management.
What Is Charge Entry?
Charge entry is a crucial step in the medical billing process, where billing teams input all necessary details about the healthcare services provided to a patient into the practice management or billing software. This includes vital information such as:
- Procedure codes (Current Procedural Terminology or CPT)
- Diagnosis codes (International Classification of Diseases or ICD-10)
- Patient information (demographics, insurance details, etc.)
- Provider information (who rendered the services)
- Dates of service (when the services were provided)
Accurately entering this data is essential because it directly influences how claims are submitted to insurance companies. Any errors at this point can lead to a ripple effect of issues, including claim rejections, delays in payment, and compliance concerns.
The Charge Entry Process in Medical Billing:
To ensure the charge entry process is smooth and error-free, healthcare practices must adopt a standardized workflow that covers every necessary step. Here’s a detailed look at the typical charge entry workflow in medical billing:
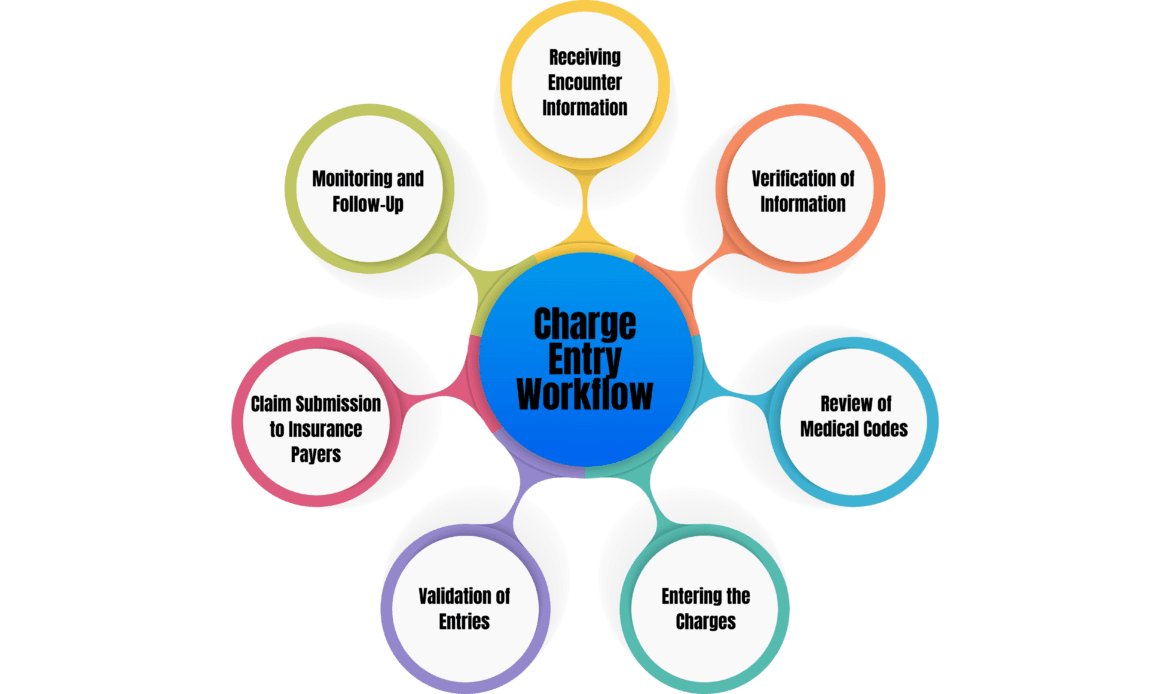
1. Receiving Encounter Information
The charge entry process begins once a healthcare provider completes the patient’s visit or procedure. After the provider documents the services rendered, this information is transferred to the medical billing team. The encounter information will include the treatments performed, diagnoses made, and other relevant details.
At this stage, the medical coder is responsible for reviewing the provider’s notes and assigning the appropriate CPT codes for the procedures performed and ICD-10 codes to represent the diagnoses. These codes will later be used for billing and insurance claims.
2. Verification of Patient Demographics and Insurance Information
Before any charges are entered, the billing team verifies that the patient’s demographic information (name, date of birth, etc.) and insurance details are accurate and up-to-date. A slight mistake in these details can cause the entire claim to be rejected by insurance companies.
At this stage, it’s important to ensure that:
- The patient’s insurance is active.
- Any co-payments or deductibles have been accounted for.
- The primary and secondary insurances are correctly listed.
3. Review of Medical Codes (CPT and ICD-10)
Once the demographic and insurance information is verified, the next step is to review the procedure and diagnosis codes assigned by the medical coder. Ensuring these codes accurately reflect the services provided is critical for successful claims submission. Any discrepancies between the procedure codes and diagnosis codes may raise red flags with insurance companies, leading to claim denials.
For example, if a CPT code for a procedure is used but the diagnosis code does not justify the necessity of that procedure, the claim will likely be denied. Accurate coding ensures compliance with insurance policies and regulatory requirements.
4. Entering the Charges
After all verifications are complete, the billing team enters the charges into the practice management or billing software. This involves inputting the CPT and ICD-10 codes along with the specific charge amounts for each service or procedure rendered. It’s critical that each charge is documented properly, as this will affect the reimbursement rate from the insurance company.
Careful attention to detail is required at this step, as any discrepancies in the data—such as entering an incorrect code or charge—can lead to billing delays or underpayments. To minimize errors, some practices use automation tools within their billing software to flag potential issues before submission.
5. Validation of Entries
Once the charges are entered, the data undergoes a validation process. This step ensures that all information entered into the system is accurate and complete. Practices often employ automated systems to review the claims for common errors, such as missing codes, incorrect patient details, or invalid insurance information.
This review acts as a final quality control check before the claim is submitted to the insurance company. It ensures that the charges entered match the documented services and diagnoses, thereby reducing the likelihood of claim rejections.
6. Claim Submission to Insurance Payers
Once the charges have been reviewed and validated, the next step is to submit the claim to the appropriate insurance payer. In most cases, this is done electronically through an Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) system. The EDI system transfers the claim data directly to the insurance company, allowing for faster processing.
At this point, the insurance payer will evaluate the claim to determine whether the services are covered under the patient’s plan and if the submitted codes are correct. Assuming everything is in order, the payer will issue payment to the healthcare provider. However, any errors in the claim will result in denials or payment delays.
7. Monitoring and Follow-Up
The final step in the charge entry workflow involves monitoring the submitted claims to ensure they are processed in a timely manner. If any issues arise—such as claim denials, rejections, or underpayments—the billing team must follow up promptly. This often involves investigating the reason for denial, correcting any errors, and resubmitting the claim.
Effective follow-up is critical to maintaining a smooth revenue cycle, as it ensures that any problems with the claims are resolved quickly and that payment is received without undue delay.
Why Is Charge Entry So Important?
The charge entry process is one of the most critical steps in the medical billing workflow. If done correctly, it can significantly enhance a practice’s revenue cycle. However, errors in charge entry can lead to several problems that can negatively affect a practice’s financial health.
1. Prevents Claim Denials and Rejections
The accuracy of the information entered during charge entry is directly related to the approval or denial of claims. Mistakes such as incorrect patient details, wrong codes, or mismatched information between the procedure and diagnosis can result in claim denials. Each denied or rejected claim requires additional effort to correct, which adds to administrative costs and delays reimbursement.
2. Speeds Up Reimbursement
Timely and accurate charge entry speeds up the overall claims process. Claims submitted with correct and validated data are processed more quickly by insurance payers, leading to faster reimbursements. This helps practices maintain a steady cash flow, which is essential for day-to-day operations.
3. Improves Revenue Cycle Efficiency
Charge entry plays a pivotal role in the overall revenue cycle management (RCM) of a medical practice. By minimizing errors during this step, practices can reduce the time spent on correcting and resubmitting claims. This leads to more efficient billing processes and ultimately maximizes revenue.
4. Reduces Administrative Workload
Errors during charge entry increase the administrative burden on billing teams. Staff members must spend time investigating denials, making corrections, and resubmitting claims. By focusing on accuracy during the initial charge entry process, practices can reduce the need for rework and free up staff to focus on other critical tasks.
5. Enhances Compliance and Reduces Legal Risks
Incorrect charge entry can lead to non-compliance with insurance and healthcare regulations. Overcharging, undercoding, or entering incorrect data can raise red flags, triggering audits or penalties. By ensuring that charge entry is accurate and compliant with the latest billing regulations, healthcare practices reduce the risk of financial penalties or legal repercussions.
The Top Four Common Errors to Avoid in Charge Entry:
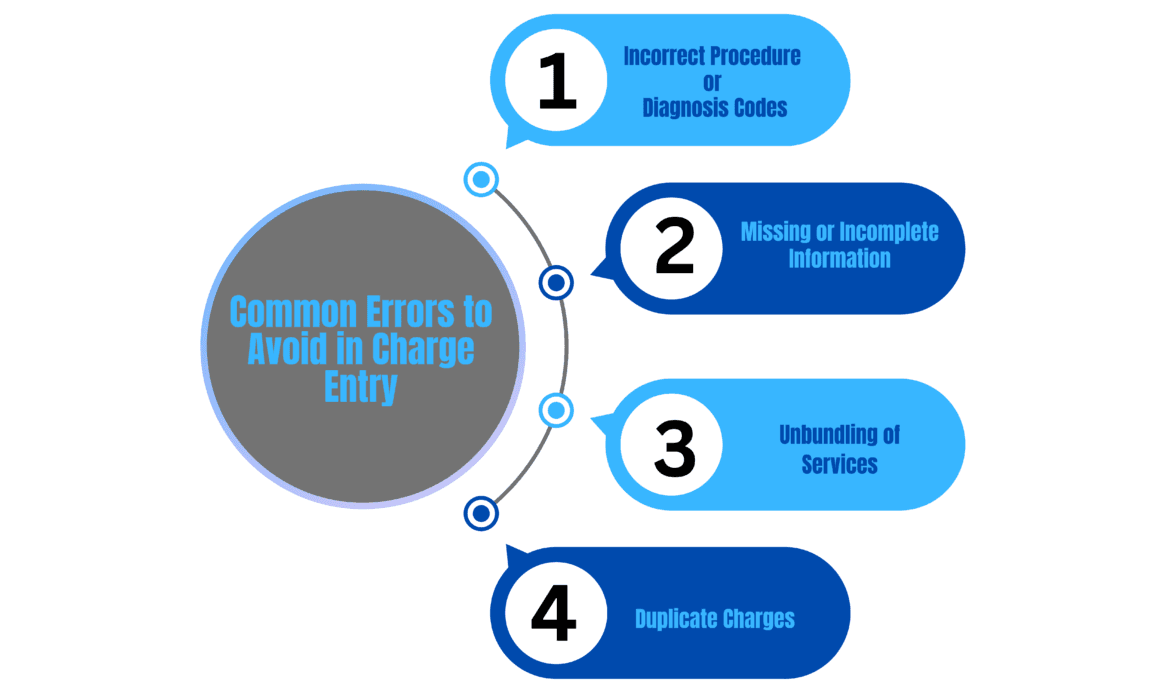
1. Incorrect Procedure or Diagnosis Codes
Entering incorrect CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) or ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) codes is one of the most prevalent errors in charge entry. This often occurs due to misunderstandings about the services provided or miscommunication between healthcare providers and billing staff. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to ensure that codes accurately reflect the services rendered. This can be achieved by:
- Cross-Referencing: Always cross-reference codes with the clinical documentation before submission.
- Continuous Training: Provide ongoing training for coding staff to keep them updated on coding guidelines and best practices.
- Utilizing Coding Software: Invest in advanced coding software that can suggest appropriate codes based on the services documented.
2. Missing or Incomplete Information
Claims submitted with missing or incomplete information, such as patient demographics or insurance details, are likely to be rejected. This often happens when billing staff rush through data entry or fail to verify necessary information. To avoid this mistake:
- Comprehensive Checklists: Use checklists to ensure all required fields are filled before submitting claims.
- Verification Process: Implement a verification process to confirm that patient information, such as insurance details and demographic data, is complete and accurate.
- Regular Updates: Regularly update and maintain patient information to prevent lapses or inaccuracies.
3. Unbundling of Services
Unbundling refers to the practice of billing separately for services that should be billed together under a bundled code. This error often leads to claim denials and may trigger audits. Billing staff should be trained to understand the rules regarding bundled billing and ensure services are coded and billed appropriately.
4. Duplicate Charges
Entering the same charge multiple times for the same service is a common mistake that can lead to payment disputes and claim denials. Duplicate charges may arise from oversight or miscommunication among billing staff. To prevent this issue:
- Automated Systems: Use automated billing systems that can flag duplicate entries before submission.
- Cross-Verification: Encourage billing staff to cross-verify charges against submitted claims to catch any duplicates.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of submitted claims to identify and rectify any duplicate entries, ensuring the billing process remains clean and efficient.
Best Practices for Accurate Charge Entry:
To ensure accuracy and minimize errors during the charge entry process, healthcare practices should follow these best practices:
- Regular Staff Training: Billing and coding staff should receive ongoing training to stay current with changes in medical codes, insurance policies, and billing software updates. Regular training helps prevent coding errors and ensures that the team is well-versed in the latest best practices.
- Automated Billing Software: Many billing systems now offer automation tools that can validate entries, flag potential issues, and streamline the charge entry process. Automation reduces human error and increases efficiency by handling repetitive tasks.
- Implement Double-Checking Systems: Having a second team member review charge entries before submission can help catch errors early in the process. This extra layer of scrutiny ensures that all data is accurate and complete before the claim is submitted.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Regular audits of the charge entry process can help identify areas where errors are occurring and provide insights for improvement. This proactive approach ensures that billing practices remain efficient and error-free over time.
- Stay Updated on Coding and Billing Changes: Medical billing codes and insurance policies frequently change. Staying informed about these updates ensures that your practice is using the correct codes and following the latest guidelines when entering charges.
Role of Technology in Charge Entry in Medical Billing?
1. Automated Billing Systems
Automated billing systems have revolutionized the charge entry process by reducing manual data entry tasks. By integrating with electronic health records (EHR) and practice management systems, these solutions automatically capture charge data, eliminating the need for healthcare providers to enter information manually. This not only speeds up the billing process but also significantly reduces the risk of human errors, such as incorrect entries or missed charges. With automation, billing teams can focus on more complex tasks, enhancing overall productivity and accuracy.
2. Real-Time Data Validation
Real-time data validation features in modern billing software provide immediate feedback during the charge entry process. As billing staff enter charges, the system checks for inconsistencies or errors in real-time, such as missing codes or incorrect patient information. This immediate error-checking capability allows staff to correct mistakes on the spot, greatly reducing the likelihood of claim denials caused by erroneous data. The result is a smoother billing process, faster claim submissions, and improved revenue cycle management.
3. Coding Software
Advanced coding software plays a crucial role in enhancing charge entry accuracy. These tools provide up-to-date coding databases, allowing medical coders to select the appropriate CPT and ICD-10 codes based on the services rendered. By utilizing these resources, billing teams can ensure compliance with current coding standards and reduce the risk of incorrect coding, which can lead to claim denials and delays in reimbursement. Furthermore, some coding software includes built-in checks and suggestions, further enhancing accuracy and efficiency in the charge entry process.
4. Electronic Claim Submission
The ability to submit claims electronically has transformed the charge entry process. With electronic claim submission, healthcare practices can transmit billing information directly to payers, expediting the claims process. This technology not only accelerates payment timelines but also provides immediate confirmation of receipt, allowing billing teams to track claims efficiently. In addition, electronic submissions reduce the administrative burden associated with paper claims, such as printing, mailing, and filing, ultimately streamlining the entire billing workflow.
5. Enhanced Reporting and Analytics
Modern billing systems offer robust reporting and analytics capabilities that provide valuable insights into charge entry performance. These features enable healthcare practices to track key metrics, such as claim denial rates and processing times, allowing them to identify trends and areas for improvement. By leveraging data-driven insights, practices can optimize their billing processes, implement targeted training for staff, and develop strategies to minimize errors. Enhanced reporting not only improves the efficiency of charge entry but also contributes to better financial management and revenue optimization.
Conclusion:
Charge entry is the foundation of the medical billing process, and its importance cannot be overstated. Errors at this stage can have far-reaching consequences, leading to denied claims, delayed payments, and revenue losses that affect the financial stability of healthcare practices. By following a structured charge entry workflow and adhering to best practices, medical practices can ensure smooth billing processes, timely reimbursements, and overall revenue cycle efficiency.
The charge entry process is not just about inputting data—it’s about safeguarding the financial health of the practice. Investing time and resources into perfecting this process will lead to fewer billing issues, enhanced compliance, and ultimately a more profitable healthcare organization.